API Documentation¶
The Ratel API sets up a PETSc DM object with the data to run a SNES or TS solver for solid mechanics problems. This DM is set for a SNES or TS via SNESSetDM or TSSetDM to provide a complete solver for a solid mechanics problem.
The API also includes functions to set sensible defaults for the TS, SNES, and KSP as well as set up geometric multigrid with PCMG.
The default options depend upon the RatelSolverType.
Lastly, the Ratel API includes convenience functions to facilitate computing model quantities of interest. These quantities of interest can be monitored on every time step via command line options or computed at the end of the solve with the convenience functions.
Ratel Public API¶
The public API provides core functionality for users.
- Core Ratel Functions
RatelSolverTypeRatelMethodTypeRatelFormulationTypeRatelForcingTypeRatelInitialConditionTypeRatelPMultigridCoarseningTypeRatelPointLocationTypeRatelMPMProjectionTypeRatelMPMInitializationTypeRatelMPMStabilizationTypeRatelDirectionTypeRatelOutputFieldsTypeRatelSolverTypesRatelMethodTypesRatelMethodTypesCLRatelForcingTypesRatelForcingTypesCLRatelInitialConditionTypesRatelPMutigridCoarseningTypesRatelPMultigridCoarseningTypesCLRatelPointLocationTypesCLRatelMPMProjectionTypesRatelMPMProjectionTypesCLRatelMPMInitializationTypesRatelMPMInitializationTypesCLRatelMPMStabilizationTypesRatelMPMStabilizationTypesCLRatelDirectionTypesCLRatelElasticityDualOutputFieldsComponentNamesRatelViewerWriteTimestep_VTKSeries()RatelTSMonitorStrainEnergy()RatelViewerWriteSurfaceForce()RatelTSMonitorSurfaceForceCellToFace()RatelTSMonitorSurfaceForce()RatelTSMonitorSurfaceForcePerFace()RatelTSMonitorOutputFields()RatelDMSwarmView_WriteDMInfo()RatelDMSwarmView_WriteField_Binary()RatelDMSwarmView_WriteField()RatelDMSwarmSubViewerCreate()RatelTSMonitorSwarm()RatelTSMonitorSwarmSolution()RatelTSMonitorCheckpoint_MPM()RatelTSMonitorCheckpoint()RatelCheckpointDataRead()RatelCheckpointDataLoadSolution()RatelCheckpointDataDestroy()RatelCheckpointCtxCreateFromOptions()RatelCheckpointCtxCreate()RatelCheckpointCtxDestroy()RatelViewerWriteHeader_CSV()RatelViewerWriteHeader_VTKSeries()RatelViewerWriteFooter_VTKSeries()RatelViewerWriteHeader_XDMF()RatelViewerWriteFooter_XDMF()RatelGetViewerInfo()RatelViewerStringIsCSV()RatelViewerStringIsXDMF()RatelLoadViewerFromCheckpoint_CSV()RatelLoadViewerFromCheckpoint_XDMF()RatelViewerCreateFromOptions()RatelViewerListCreateFromOptions()RatelViewerCreate()RatelViewerDestroy()RatelViewerWriteHeader()RatelViewerWriteFooter()RatelViewerGetSequenceFilename()RatelViewerShouldWrite()RatelViewersCreateFromOptions()RatelViewersCreate()RatelViewersDestroy()RatelHasMMS()RatelIsCeedBP()RatelComputeMMSL2Error()RatelViewMMSL2ErrorFromOptions()RatelGetExpectedStrainEnergy()RatelGetExpectedMaxDisplacement()RatelGetExpectedFaceSurfaceForce()RatelGetExpectedFaceCentroid()RatelComputeStrainEnergyError()RatelComputeMaxDisplacementError()RatelViewMaxSolutionValuesErrorFromOptions()RatelComputeFaceForceErrors()RatelViewSurfaceForceAndCentroidErrorFromOptions()RatelComputeStrainEnergy()RatelViewStrainEnergyErrorFromOptions()RatelComputeMaxVectorValues()RatelComputeMaxSolutionValues()RatelComputeMaxOutputFields()RatelGetExpectedMaxOutputFields()RatelComputeMaxOutputFieldsError()RatelViewMaxOutputFieldsErrorByNameFromOptions()RatelViewVolumeErrorFromOptions()RatelViewOutputFieldsFromOptions()RatelGetSurfaceForceFaces()RatelComputeSurfaceForcesCellToFace()RatelComputeSurfaceForces()RatelComputeSurfaceCentroids()RatelComputeVolume()RatelGetOutputFields()RatelRestoreOutputFields()RatelTSSetup()RatelTSSetFromOptions()RatelKSPSetup()RatelSNESSetup()RatelSetupZeroInitialCondition()RatelSetupNonZeroInitialConditionMMS()RatelSetupNonZeroInitialCondition()RatelTSSetupInitialCondition()RatelSNESSetupInitialCondition()RatelTSCheckpointFinalSolutionFromOptions()RatelSNESCheckpointFinalSolutionFromOptions()RatelGetVersion()RatelRegisterLogEvents()RatelInit()RatelView()RatelViewBanner()RatelDestroy()RatelDMCreate()RatelSetNonSPD()RatelLogStagePushDebug()RatelLogStagePopDebug()RATEL_VERSION_MAJORRATEL_VERSION_MINORRATEL_VERSION_PATCHRATEL_VERSION_RELEASERATEL_VERSION_GERatelUnitsRatel
Ratel Internal API¶
The internal API builds composite CeedOperator for the residual, Jacobian, and output fields evaluation.
These composite CeedOperator are used to set the appropriate DMSNES or DMTS options, depending upon the RatelSolverType.
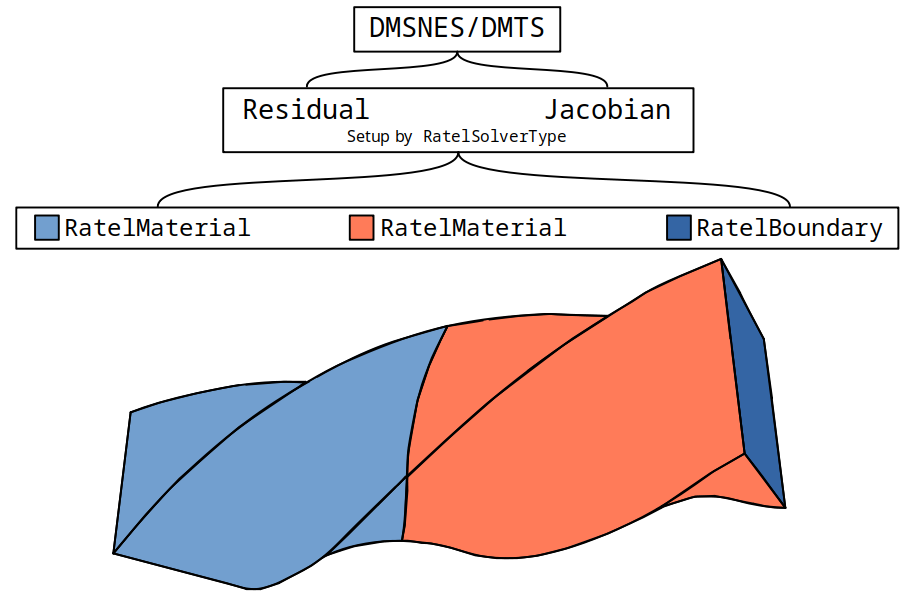
The internal API is organized around RatelMaterial, separate material regions in the domain.
See the Using Ratel section of the documentation for details on how the user specifies a material region with model parameters for the mesh.
Each RatelMaterial is responsible for adding volumetric terms to the residual, Jacobian, and output fields evaluation operators as well as any surface terms that require volumetric or material model values.
Additionally, each RatelMaterial is responsible for building and modifying corresponding preconditioner components, as needed.
Boundary and forcing terms that do not require volumetric or material model parameters, such as Dirichlet boundary conditions, are handled separately from a RatelMaterial.
New RatelMaterial are added by creating a file src/materials/new-material.c with the material model data, material creation function, and material registration function.
Any new QFunction source files go in include/ratel/qfunctions, and the material is added to src/materials/ratel-model-list.h.
Any new CeedQFunction created for a RatelMaterial must list their CeedQFunction inputs and outputs in the following order, omitting any inputs or outputs that are not applicable:
- Inputs:
Quadrature point data, such as integration weights and change of coordinate matrices
State data, such as plastic state
Stored values, such as residual evaluation data stored for reuse in the Jacobian
Model variables and their derivatives, as needed
Additional inputs as needed by the specific CeedQFunction
- Outputs:
Current state data
Stored values for material model
Action of the operator the QFunction represents
Additional outputs as needed by the specific CeedQFunction
- The
RatelModelassociated with theRatelMaterialcan specify the following CeedQFunction setup_q_data_volume - volumetric quadrature data setup
setup_q_data_surface - surface quadrature data for integration setup
setup_q_data_surface_grad - surface quadrature data for gradients setup
residual_u - nonlinear residual evaluation
residual_ut - nonlinear residual evaluation time derivative term
residual_utt - nonlinear residual evaluation time second derivative term
jacobian - linear Jacobian evaluation
jacobian_block - block suboperators by field for Jacobian evaluation
strain_energy - strain energy evaluation
projected_output_fields - output fields projected from quadrature space to the dual space
dual_output_fields - output fields computed on the dual space
contact_residual_u - residual evaluation for contact boundary conditions
contact_jacobian - Jacobian evaluation for contact boundary conditions
mms_boundary - MMS Dirichlet boundary values
mms_forcing - MMS forcing term
mms_error - MMS error against true solution
surface_force_cell_to_face - state in cells used to evaluate strain and stresses on the face, stress integrated to get forces on the surface
Numerical solvers¶
These functions setup the numerical solver and preconditioner.
- Numerical Solvers
PCPMG_CLASSIDPCPMG_SetupRATEL_ProlongRATEL_Prolong_CeedOpRATEL_RestrictRATEL_Restrict_CeedOpRatelRegisterPMultigridLogEvents()RatelPCSetFromOptions_PMG()RatelSetupMultigridLevel()RatelPCPMGCreateMGHeirarchy()RatelPCPMGCreate()RatelPCReset_PMG()RatelPCSetUp_PMG()RatelPCPMGSetReuseCoarseMat()RatelPCPMGGetReuseCoarseMat()RatelPCView_PMG()RatelPCApply_PMG()RatelPCApplyTranspose_PMG()RatelPCMatApply_PMG()RatelPCDestroy_PMG()RatelPCPMGContextDestroy()RatelPCRegisterPMG()RatelDMSetupSolver()
Material models¶
These functions setup the material regions in the mesh.
- Material Models
RatelMaterialSetupMultigridLevelFunctionRatelComputef1_cppRatelComputef1_fwd_cppRatelComputef1RatelComputef1_fwdRatelComputeDamagef1RatelComputeDamagef1_fwdRatelComputeDamagef0RatelComputeDamagef0_fwdRatelComputef1_MixedRatelComputedf1_fwd_MixedRatelComputeg0_MixedRatelComputedg0_fwd_MixedRatelComputeOutputFieldsMixedStressRatelComputeOutputFieldsStressRatelComputef1_PoromechanicsRatelComputedf1_fwd_PoromechanicsRatelComputeg0_PoromechanicsRatelComputedg0_fwd_PoromechanicsRatelComputeg1_PoromechanicsRatelComputedg1_fwd_PoromechanicsRatelComputedf0_fwd_PoroelastodynamicsRatelComputedg0_fwd_PoroelastodynamicsRatelComputedg1_fwd_Poroelastodynamicselasticity_damage_param_data_privateelasticity_damage_param_datamixed_anisotropic_neo_hookean_param_data_privatemixed_anisotropic_neo_hookean_param_datamixed_neo_hookean_param_data_privatemixed_neo_hookean_param_datamixed_ogden_param_data_privatemixed_ogden_param_datamms_ceed_bps_param_data_privatemms_ceed_bps_param_datamms_linear_elasticity_param_data_privatemms_linear_elasticity_param_datamms_linear_poromechanics_param_data_privatemms_linear_poromechanics_param_datamooney_rivlin_param_data_privatemooney_rivlin_param_dataneo_hookean_shock_scalar_param_data_privateneo_hookean_shock_scalar_param_dataneo_hookean_param_data_privateneo_hookean_param_dataogden_param_data_privateogden_param_dataplasticity_damage_param_data_privateplasticity_damage_param_dataplasticity_param_data_privateplasticity_param_dataporomechanics_neo_hookean_param_data_privateporomechanics_neo_hookean_param_dataporomechanics_linear_param_data_privateporomechanics_linear_param_datatriclinic_anisotropic_param_data_privatetriclinic_anisotropic_param_dataviscoelasticity_damage_param_data_privateviscoelasticity_damage_param_dataviscoelasticity_param_data_privateviscoelasticity_param_dataDMSwarmPICField_volumeDMSwarmPICField_JDMSwarmPICField_materialRatelDMLabel_MPMMaterialsRatelDMLabel_MPMBoundaryCellsRatelDMLabel_MPMBoundaryFacesRatelDMLabel_MPMDomainBoundaryFacesRestrictBoundingBox()SetupSurfaceGeometryBounded()SetupSurfaceForceGeometry()SetupSurfaceGeometry()UpdateVolume_MPM()UpdateVolume_Damage_MPM()SetupVolumeGeometryMPM()CoordinatesToReferenceNewtonUpdate()SetupVolumeGeometrySymmetricMPM()SetupVolumeGeometrySymmetric()SetupVolumeGeometry()Residual_CEED_BP1()Jacobian_CEED_BP1()OutputFields_CEED_BP1()Residual_CEED_BP2()Jacobian_CEED_BP2()OutputFields_CEED_BP2()Residual_CEED_BP3()Jacobian_CEED_BP3()OutputFields_CEED_BP3()Residual_CEED_BP4()Jacobian_CEED_BP4()OutputFields_CEED_BP4()DualOutputFields()ElasticityResidual()ElasticityJacobian()ElasticityDamageResidual()ElasticityDamageJacobian()ElasticityDualOutputFields()RatelComputeHenckyStrain()RatelComputeHenckyStrain_fwd()RatelKirchhoffTau_Hencky()RatelHenckySecondKirchhoffStress()RatelHenckySecondKirchhoffStress_fwd()RatelHenckyStrainEigenvalues()RatelHencky_dbedF_Symmetric()RatelHencky_dedb_Eigenvalues()RatelHenckyKirchhoffStressSymmetric_fwd()RatelStrainEnergy_ElasticityHencky()StrainEnergy_ElasticityHencky()OutputFields_ElasticityHencky()f1_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()df1_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal_Residual()ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal_Jacobian()PsiPlus_Hencky_Principal()PsiPlus_Hencky_Principal_fwd()OutputFields_ElasticityHenckyDamage()StrainEnergy_ElasticityHenckyDamage()ElasticityDamageDualOutputFields_Hencky()ElasticityDamageResidual_ut_HenckyCurrent()ElasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal_Residual()ElasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal_Jacobian()ElasticityDamageResidual_ut_HenckyInitial()ElasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal_Residual()ElasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal_Jacobian()ElasticityDamageContactResidual_HenckyInitialPrincipal()ElasticityDamageContactJacobian_HenckyInitialPrincipal()ContactBCsResidualElasticityDamage_HenckyInitialPrincipal()ContactBCsJacobianElasticityDamage_HenckyInitialPrincipal()f1_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()df1_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal_Residual()ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal_Jacobian()ContactBCsResidualElasticity_HenckyInitialPrincipal()ContactBCsJacobianElasticity_HenckyInitialPrincipal()RatelKirchhoffTau_IsochoricMooneyRivlin()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_IsochoricMooneyRivlin()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_IsochoricMooneyRivlin_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_IsochoricMooneyRivlin()RatelStrainEnergy_IsochoricMooneyRivlin()StrainEnergy_IsochoricMooneyRivlin()OutputFieldsStress_IsochoricMooneyRivlin()OutputFields_IsochoricMooneyRivlin()f1_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrent()df1_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrent()ElasticityResidual_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrent()f1_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()df1_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()ElasticityResidual_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()ElasticityJacobian_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()ContactBCsResidual_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()RatelKirchhoffTau_IsochoricNeoHookean()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_IsochoricNeoHookean()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_IsochoricNeoHookean_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_IsochoricNeoHookean()RatelStrainEnergy_IsochoricNeoHookean()StrainEnergy_IsochoricNeoHookean()OutputFieldsStress_IsochoricNeoHookean()OutputFields_IsochoricNeoHookean()f1_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrent()df1_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityResidual_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrent()f1_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()df1_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityResidual_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityJacobian_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()ContactBCsResidual_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()RatelKirchhoffTau_IsochoricOgden()SecondKirchhoffStress_IsochoricOgden()SecondKirchhoffStress_IsochoricOgden_fwd()RatelComputeKirchhoffTau_IsochoricOgden_fwd()RatelStrainEnergy_IsochoricOgden()StrainEnergy_IsochoricOgden()OutputFieldsStress_IsochoricOgden()OutputFields_IsochoricOgden()RatelStrainEnergy_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_Enzyme()RatelKirchhofftau_sym_IsochoricOgden_AD()Rateldtau_fwd_IsochoricOgden_AD()f1_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_Enzyme()df1_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_Enzyme()ElasticityResidual_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_Enzyme()ElasticityJacobian_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_Enzyme()f1_IsochoricOgdenCurrent()df1_IsochoricOgdenCurrent()ElasticityResidual_IsochoricOgdenCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_IsochoricOgdenCurrent()f1_IsochoricOgdenInitial()df1_IsochoricOgdenInitial()ElasticityResidual_IsochoricOgdenInitial()ElasticityJacobian_IsochoricOgdenInitial()ContactBCsResidual_IsochoricOgdenInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_IsochoricOgdenInitial()RatelIsochoricKirchhoffTau_MooneyRivlin()RatelIsochoricSecondKirchhoffStress_MooneyRivlin()RatelIsochoricSecondKirchhoffStress_MooneyRivlin_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTransposeIsochoric_MooneyRivlin()RatelIsochoricKirchhoffTau_NeoHookean()RatelIsochoricSecondKirchhoffStress_NeoHookean()RatelIsochoricSecondKirchhoffStress_NeoHookean_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTransposeIsochoric_NeoHookean()RatelIsochoricKirchhoffTau_Ogden()RatelIsochoricSecondKirchhoffStress_Ogden()RatelIsochoricSecondKirchhoffStress_Ogden_fwd()RatelIsochoricKirchhoffTau_Ogden_fwd()PsiPlus_Linear()PsiPlus_Linear_fwd()ComputeDegradedStress_Linear()ComputeDegradedStress_Linear_fwd()ElasticityDamageResidual_ut_Linear()f0_DamageLinear()f1_u_DamageLinear()f1_phi_DamageLinear()f1_DamageLinear()df0_DamageLinear()df1_u_DamageLinear()df1_phi_DamageLinear()df1_DamageLinear()ElasticityDamageResidual_Linear()ElasticityDamageJacobian_Linear()f1_ElasticityDamageLinear_Contact()df1_ElasticityDamageLinear_Contact()ContactBCsResidualElasticityDamage_Linear()ContactBCsJacobianElasticityDamage_Linear()ElasticityDamageOutputFields_Linear()ElasticityDamageStrainEnergy_Linear()ElasticityDamageDualOutputFields_Linear()ElasticityDualOutputFields_Linear()f1_Linear()df1_Linear()ElasticityResidual_Linear()ElasticityJacobian_Linear()ContactBCsResidual_Linear()ContactBCsJacobian_Linear()StrainEnergy_Linear()OutputFields_Linear()SurfaceForceCellToFace_Linear()RatelComputePhiAnisoTerms()RatelComputeStructureTensor_Current()RatelAnisotropicKirchoffTau_NeoHookean()RatelComputeFdSFTransposeAnisotropic_NeoHookean()RatelKirchhoffTau_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookean()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookean()RatelStrainEnergy_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookean()StrainEnergy_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookean()OutputFields_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookean()f1_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()g0_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()df1_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()dg0_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityResidual_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityPC_uu_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityPC_pp_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()MixedElasticityResidual()MixedElasticityJacobian()f1_MixedLinear()g0_MixedLinear()df1_MixedLinear()dg0_MixedLinear()ElasticityResidual_MixedLinear()ElasticityJacobian_MixedLinear()f1_MixedLinear_Contact()df1_MixedLinear_Contact()ContactBCsResidual_MixedLinear()ContactBCsJacobian_MixedLinear()StrainEnergy_MixedLinear()OutputFields_MixedLinear()ElasticityPC_uu_MixedLinear()ElasticityPC_pp_MixedLinear()RatelKirchhoffTau_MixedNeoHookean()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MixedNeoHookean()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MixedNeoHookean_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_MixedNeoHookean()RatelStrainEnergy_MixedNeoHookean()StrainEnergy_MixedNeoHookean()OutputFieldsStress_MixedNeoHookean()OutputFields_MixedNeoHookean()f1_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()g0_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()df1_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()dg0_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityResidual_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityPC_uu_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityPC_pp_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent()f1_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()g0_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()df1_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()dg0_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityResidual_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityJacobian_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()f1_MixedNeoHookeanInitial_Contact()df1_MixedNeoHookeanInitial_Contact()ContactBCsResidual_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityPC_uu_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityPC_pp_MixedNeoHookeanInitial()RatelKirchhoffTau_MixedNeoHookeanPL()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MixedNeoHookeanPL()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MixedNeoHookeanPL_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_MixedNeoHookeanPL()RatelStrainEnergy_MixedNeoHookeanPL()StrainEnergy_MixedNeoHookeanPL()OutputFields_MixedNeoHookeanPL()f1_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()g0_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()df1_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()dg0_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()ElasticityResidual_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()ElasticityPC_uu_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()ElasticityPC_pp_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()f1_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()g0_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()df1_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()dg0_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()ElasticityResidual_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()ElasticityJacobian_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()f1_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial_Contact()df1_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial_Contact()ContactBCsResidual_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()ElasticityPC_uu_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()ElasticityPC_pp_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()RatelKirchhoffTau_MixedOgden()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MixedOgden()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MixedOgden_fwd()RatelStrainEnergy_MixedOgden()StrainEnergy_MixedOgden()OutputFieldsStress_MixedOgden()OutputFields_MixedOgden()f1_MixedOgdenInitial()g0_MixedOgdenInitial()df1_MixedOgdenInitial()dg0_MixedOgdenInitial()ElasticityResidual_MixedOgdenInitial()ElasticityJacobian_MixedOgdenInitial()f1_MixedOgdenInitial_Contact()df1_MixedOgdenInitial_Contact()ContactBCsResidual_MixedOgdenInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_MixedOgdenInitial()ElasticityPC_uu_MixedOgdenInitial()ElasticityPC_pp_MixedOgdenInitial()MixedElasticityOutputFields()RatelVolumetricKirchhoffTau_Mixed_PL()RatelVolumetricSecondKirchhoffStress_Mixed_PL()RatelVolumetricSecondKirchhoffStress_Mixed_PL_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTransposeVolumetric_Mixed_PL()RatelVolumetricKirchhoffTau_Mixed()RatelVolumetricSecondKirchhoffStress_Mixed()RatelVolumetricSecondKirchhoffStress_Mixed_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTransposeVolumetric_Mixed()RatelKirchhoffTau_MooneyRivlin()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MooneyRivlin()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_MooneyRivlin_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_MooneyRivlin()RatelStrainEnergy_MooneyRivlin()StrainEnergy_MooneyRivlin()OutputFieldsStress_MooneyRivlin()OutputFields_MooneyRivlin()f1_MooneyRivlinCurrent()df1_MooneyRivlinCurrent()ElasticityResidual_MooneyRivlinCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_MooneyRivlinCurrent()f1_MooneyRivlinInitial()df1_MooneyRivlinInitial()ElasticityResidual_MooneyRivlinInitial()ElasticityJacobian_MooneyRivlinInitial()ContactBCsResidual_MooneyRivlinInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_MooneyRivlinInitial()ElasticityDualOutputFields_MPM()StrainEnergy_MPM_NeoHookean()OutputFields_MPM_NeoHookean()SetPointFields_MPM_NeoHookean()f1_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrent()df1_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityResidual_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityDamageOutputFields_NeoHookean_MPM()ElasticityDamageStrainEnergy_NeoHookean_MPM()SetPointFields_MPM_ElasticityDamageNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityDamageResidual_ut_NeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()f0_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()f1_u_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()f1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()f1_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()df0_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()df1_u_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()df1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()df1_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()ElasticityDamageResidual_NeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()ElasticityDamageJacobian_NeoHookeanCurrent_MPM()SetPointFields_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()f1_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()df1_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()ElasticityResidual_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()ElasticityJacobian_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()StrainEnergy_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()OutputFields_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()SurfaceForceCellToFace_NeoHookean()RatelKirchhoffTau_NeoHookean()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_NeoHookean()RatelSecondKirchhoffStress_NeoHookean_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_NeoHookean()RatelStrainEnergy_NeoHookean()StrainEnergy_NeoHookean()OutputFieldsStress_NeoHookean()OutputFields_NeoHookean()f1_NeoHookeanCurrent_AD_ADOLC()df1_NeoHookeanCurrent_AD_ADOLC()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanCurrent_AD_ADOLC()ElasticityJacobian_NeoHookeanCurrent_AD_ADOLC()RatelStrainEnergy_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_Enzyme()RatelKirchhofftau_sym_NeoHookean_AD()Rateldtau_fwd()f1_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_Enzyme()df1_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_Enzyme()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_Enzyme()ElasticityJacobian_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_Enzyme()f1_NeoHookeanCurrent()df1_NeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_NeoHookeanCurrent()PsiPlus_NeoHookean()PsiPlus_NeoHookeanInitial_fwd()ComputeDegradedSecondKirchhoffStress_NeoHookean()ComputeDegradedSecondKirchhoffStress_NeoHookean_fwd()ComputeDegradedKirchhoffTau_NeoHookean()PsiPlus_NeoHookeanCurrent_fwd()RatelComputeDegradedFdSFTranspose_NeoHookean()ElasticityDamageStrainEnergy_NeoHookean()ElasticityDamageOutputFields_NeoHookean()ElasticityDamageDualOutputFields_NeoHookean()f1_u_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent()f1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent()f1_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent()df1_u_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent()df1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent()df1_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityDamageResidual_NeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityDamageJacobian_NeoHookeanCurrent()ElasticityDamageResidual_ut_NeoHookean()f0_DamageNeoHookean()f1_u_DamageNeoHookeanInitial()f1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanInitial()f1_DamageNeoHookeanInitial()df0_DamageNeoHookean()df1_u_DamageNeoHookeanInitial()df1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanInitial()df1_DamageNeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityDamageResidual_NeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityDamageJacobian_NeoHookeanInitial()f1_ElasticityDamageNeoHookeanInitial_Contact()df1_ElasticityDamageNeoHookeanInitial_Contact()ContactBCsResidualElasticityDamage_NeoHookeanInitial()ContactBCsJacobianElasticityDamage_NeoHookeanInitial()f1_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_ADOLC()df1_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_ADOLC()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_ADOLC()ElasticityJacobian_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_ADOLC()RatelStrainEnergy_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_Enzyme()SecondPiolaKirchhoffStress_NeoHookean_AD()S_augmentfwd()dS_fwd()f1_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_Enzyme()df1_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_Enzyme()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_Enzyme()ElasticityJacobian_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_Enzyme()f1_NeoHookeanInitial()df1_NeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanInitial()ElasticityJacobian_NeoHookeanInitial()ContactBCsResidual_NeoHookeanInitial()ContactBCsJacobian_NeoHookeanInitial()f1_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent_ut()df1_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent()ElasticityResidual_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent()ElasticityJacobian_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent()ElasticityOutputFields()RatelFormCrystalBasis()RatelTensor4MatMultSym()RatelVecRotateRodrigues()RatelMatRotationRodrigues()f1_TriclinicAnisotropicInitial()df1_TriclinicAnisotropicInitial()ElasticityResidual_TriclinicAnisotropicInitial()ElasticityJacobian_TriclinicAnisotropicInitial()StrainEnergy_TriclinicAnisotropicInitial()OutputFieldsStress_TriclinicAnisotropicInitial()OutputFields_TriclinicAnisotropicInitial()uhyper_()ElasticityResidual_UHyper()ElasticityJacobian_UHyper()StrainEnergy_UHyper()OutputFields_UHyper()VolumetricFunctionAndDerivatives()VolumetricFunctionAndDerivatives_PL()VolumetricFunctionAndDerivatives_Classical_PL()VolumetricFunctionAndDerivatives_Eipper()RatelVolumetricKirchhoffTau()RatelVolumetricSecondKirchhoffStress()RatelVolumetricSecondKirchhoffStress_fwd()RatelComputeFdSFTransposeVolumetric()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_be_trial_Symmetric()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_StrainSplit()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_Cp_Update()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_dbedF_Symmetric()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_dedb()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_KirchhoffStressSymmetric_fwd()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_dlogAdA_Symmetric()RatelComputeInternalForcePlasticity()RatelComputeYieldStress()RatelComputeHardeningSlope()RatelReturnMapping()RatelComputeDeltaPlasticStrain()RatelComputeDeltaPlasticStrain_fwd()RatelReturnMapping_vonMises()RatelReturnMapping_vonMises_fwd()RatelReturnMapping_vonMises_Principal()RatelReturnMapping_vonMises_Principal_fwd()RatelComputeFlowStress()RatelComputeFlowStress_fwd()RatelComputeDeltaGamma_vonMises()OutputFields_PlasticityHencky_Additive()StrainEnergy_PlasticityHencky_Additive()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_PrandtlElement_DeviatoricStrainUpdate()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_PrandtlElement_be_Update()OutputFields_PlasticityHencky()StrainEnergy_PlasticityHencky()psi_elastic()psi_plastic()phi()RatelKirchhoffTau_HenckyAdditive_AD()RatelComputeBeta_AD()dPhi()RatelComputeYieldStress_AD()RatelComputeVonMisesEffectiveStress()RatelComputeVonMisesEffectiveStress_delta_gamma()RatelComputeHardeningSlope_AD()RatelReturnMapping_AD()RatelKirchhoffTau_HenckyAdditive_AD_fwd()ddPhi()RatelComputePlasticMultiplier_AD_fwd()RatelComputeDeltaPlasticStrain_AD_fwd()f1_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme()df1_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme()PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme_Residual()PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme_Jacobian()ContactBCsResidualPlasticity_HenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme()ContactBCsJacobianPlasticity_HenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme()f1_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditive()df1_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditive()PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditive_Residual()PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditive_Jacobian()ContactBCsResidualPlasticity_HenckyCurrentAdditive()ContactBCsJacobianPlasticity_HenckyCurrentAdditive()f1_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()df1_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal_Residual()PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal_Jacobian()f1_PlasticityHenckyCurrent()df1_PlasticityHenckyCurrent()PlasticityHenckyCurrent_Residual()PlasticityHenckyCurrent_Jacobian()ContactBCsResidualPlasticity_HenckyCurrent()ContactBCsJacobianPlasticity_HenckyCurrent()OutputFields_PlasticityHenckyDamage()StrainEnergy_PlasticityHenckyDamage()f1_u_DamageHenckyPlasticityCurrentPrincipal()f1_phi_DamageHenckyPlasticityCurrent()f1_DamageHenckyPlasticityCurrent()df1_u_DamageHenckyPlasticityCurrentPrincipal()df1_phi_DamageHenckyPlasticityCurrent()df1_DamageHenckyPlasticityCurrent()PlasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal_Residual()PlasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal_Jacobian()PlasticityDamageResidual_ut_Hencky()f0_DamageHenckyPlasticity()f1_u_DamageHenckyPlasticityInitialPrincipal()f1_phi_DamageHenckyPlasticityInitial()f1_DamageHenckyPlasticityInitial()df0_DamageHenckyPlasticity()df1_u_DamageHenckyPlasticityInitialPrincipal()df1_phi_DamageHenckyPlasticityInitial()df1_DamageHenckyPlasticityInitial()PlasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal_Residual()PlasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal_Jacobian()f1_PlasticityDamageInitial_Contact()df1_PlasticityDamageInitial_Contact()ContactBCsResidualPlasticityDamage_HenckyInitial()ContactBCsJacobianPlasticityDamage_HenckyInitial()f1_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()df1_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal_Residual()PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal_Jacobian()ContactBCsResidualPlasticity_HenckyInitialPrincipal()ContactBCsJacobianPlasticity_HenckyInitialPrincipal()f1_PlasticityHenckyInitial()df1_PlasticityHenckyInitial()PlasticityHenckyInitial_Residual()PlasticityHenckyInitial_Jacobian()ContactBCsResidualPlasticity_HenckyInitial()ContactBCsJacobianPlasticity_HenckyInitial()f1_PlasticityLinear()df1_PlasticityLinear()PlasticityResidual_PlasticityLinear()PlasticityJacobian_PlasticityLinear()ContactBCsResidual_PlasticityLinear()ContactBCsJacobian_PlasticityLinear()StrainEnergy_PlasticityLinear()OutputFields_PlasticityLinear()PoromechanicsResidual()PoromechanicsJacobian()f1_PoromechanicsLinear()g1_PoromechanicsLinear()g0_PoromechanicsLinear()PoromechanicsResidual_Linear_ut()df1_PoromechanicsLinear()dg1_PoromechanicsLinear()dg0_PoromechanicsLinear()df0_PoroelastodynamicsLinear()dg1_PoroelastodynamicsLinear()dg0_PoroelastodynamicsLinear()PoromechanicsResidual_Linear()PoromechanicsJacobian_Linear()f1_PoromechanicsLinear_Contact()df1_PoromechanicsLinear_Contact()ContactBCsResidual_PoromechanicsLinear()ContactBCsJacobian_PoromechanicsLinear()StrainEnergy_PoromechanicsLinear()OutputFields_PoromechanicsLinear()PoromechanicsPC_uu_Linear()PoromechanicsPC_pp_Linear()PoreFluidDensity()PorosityFunctionKozenyCarman()PorosityFunctionKozenyCarman_fwd()PorosityFunctionHyperbolic()PorosityFunctionHyperbolic_fwd()RatelKirchhoffTau_PoromechanicsNeoHookean()RatelComputeFdSFTranspose_PoromechanicsNeoHookean()StrainEnergy_PoromechanicsNeoHookean()OutputFields_PoromechanicsNeoHookean()f1_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()g1_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()g0_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()PoromechanicsResidual_NeoHookeanCurrent_ut()df1_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()dg1_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()dg0_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()df0_PoroelastodynamicsNeoHookeanCurrent()dg1_PoroelastodynamicsNeoHookeanCurrent()dg0_PoroelastodynamicsNeoHookeanCurrent()PoromechanicsResidual_NeoHookeanCurrent()PoromechanicsJacobian_NeoHookeanCurrent()PoromechanicsPC_uu_NeoHookeanCurrent()PoromechanicsPC_pp_NeoHookeanCurrent()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_MaxwellElement_DeviatoricStrainUpdate()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_MaxwellElement_be_Update()RatelLogStrainInelasticity_MaxwellElement_DeviatoricStrainUpdate_fwd()OutputFields_ViscoelasticityHencky()StrainEnergy_ViscoelasticityHencky()f1_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()df1_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal_Residual()ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal_Jacobian()OutputFields_ViscoelasticityHenckyDamage()StrainEnergy_ViscoelasticityHenckyDamage()f1_u_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityCurrentPrincipal()f1_phi_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityCurrent()f1_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityCurrent()df1_u_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityCurrentPrincipal()df1_phi_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityCurrent()df1_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityCurrent()ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal_Residual()ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal_Jacobian()ViscoelasticityDamageResidual_HenckyInitial_ut()f0_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitial()f1_u_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitialPrincipal()f1_phi_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitial()f1_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitial()df0_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitial()df1_u_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitialPrincipal()df1_phi_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitial()df1_DamageHenckyViscoelasticityInitial()ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal_Residual()ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal_Jacobian()f1_ViscoelasticityDamageInitial_Contact()df1_ViscoelasticityDamageInitial_Contact()ContactBCsResidualViscoelasticityDamage_HenckyInitial()ContactBCsJacobianViscoelasticityDamage_HenckyInitial()f1_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()df1_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal_Residual()ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal_Jacobian()ContactBCsResidualViscoelasticity_HenckyInitialPrincipal()ContactBCsJacobianViscoelasticity_HenckyInitialPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_CEED_BP1()RatelRegisterModel_CEED_BP1()RatelMaterialCreate_CEED_BP2()RatelRegisterModel_CEED_BP2()RatelMaterialCreate_CEED_BP3()RatelRegisterModel_CEED_BP3()RatelMaterialCreate_CEED_BP4()RatelRegisterModel_CEED_BP4()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityIsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityIsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityIsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityIsochoricMooneyRivlinInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityIsochoricNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityIsochoricNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityIsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityIsochoricNeoHookeanInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityIsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_Enzyme()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityIsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_Enzyme()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityIsochoricOgdenCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityIsochoricOgdenCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityIsochoricOgdenInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityIsochoricOgdenInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityLinearDamage()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityLinearDamage()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityLinear()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityLinear()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMixedLinear()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMixedLinear()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMixedNeoHookeanPLInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMixedOgdenInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMixedOgdenInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMooneyRivlinCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMooneyRivlinCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMooneyRivlinInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMooneyRivlinInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMPMNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMPMNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMPMNeoHookeanDamageCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMPMNeoHookeanDamageCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityMPMTriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityMPMTriclinicAnisotropicPrevious()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanCurrentAD_ADOLC()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanCurrentAD_ADOLC()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanCurrentAD_ADOLC_C()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanCurrentAD_Enzyme()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanCurrentAD_Enzyme()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanDamageCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanDamageCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanDamageInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanDamageInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitialAD_ADOLC()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitialAD_ADOLC()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitialAD_ADOLC_C()RatelCheckTapeSize_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitialAD_Enzyme()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitialAD_Enzyme()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitialAD_Enzyme()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityNeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityNeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityTriclinicAnisotropicInitial()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityTriclinicAnisotropicInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_ElasticityUHyper()RatelRegisterModel_ElasticityUHyper()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_ElasticityDamage()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_ElasticityDamage()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookean()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookean()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_MixedNeoHookean()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_MixedNeoHookean()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_MixedOgden()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_MixedOgden()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_MMS_CEED_BPs()RatelMMSParamsContextCreate_CEED_BPs()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_MMS_Elasticity_Linear()RatelMMSParamsContextCreate_Elasticity_Linear()RatelMMSParamsContextCreate_Elasticity_MixedLinear()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_MMS_PoromechanicsLinear()RatelMMSParamsContextCreate_PoromechanicsLinear()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_MooneyRivlin()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_MooneyRivlin()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_NeoHookeanShockScalar()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_NeoHookeanShockScalar()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_NeoHookean()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_NeoHookean()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_Ogden()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_Ogden()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_PlasticityDamage()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_PlasticityDamage()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_Plasticity()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_Plasticity()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_PoromechanicsNeoHookean()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_PoromechanicsNeoHookean()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_PoromechanicsLinear()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_PoromechanicsLinear()RatelRandomGetValuesNormal()RatelMaterialCreateRandomParameters_TriclinicAnisotropic()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_TriclinicAnisotropic()RatelElasticityTensorView()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_TriclinicAnisotropic()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_ViscoelasticityDamage()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_ViscoelasticityDamage()RatelCeedParamsContextCreate_Viscoelasticity()RatelMaterialParamsContextCreate_Viscoelasticity()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_Enzyme()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditive()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditive()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityHenckyInitial()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityHenckyInitial()RatelMaterialCreate_PlasticityLinear()RatelRegisterModel_PlasticityLinear()RatelMaterialCreate_PoromechanicsLinear()RatelRegisterModel_PoromechanicsLinear()RatelMaterialCreate_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelRegisterModel_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent()RatelMaterialCreate_FEM()RatelSolutionDMSetup_FEM()RatelEnergyDMSetup_FEM()RatelOutputFieldsDMsSetup_FEM()RatelSurfaceForceCellToFaceDMSetup_FEM()RatelDMSetupByOrder_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupVolumeQData_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupSurfaceGradientQData_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupResidualSuboperators_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupJacobianSuboperator_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupJacobianMultigridLevel_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupJacobianBlockSuboperator_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupStrainEnergySuboperator_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupOutputFieldsSuboperators_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupSurfaceForceCellToFaceSuboperators_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupMMSErrorSuboperator_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupForcingSuboperator_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupForcingEnergySuboperator_FEM()RatelMaterialSetupOutputFields()RatelMaterialCreate()RatelMaterialView()RatelModelDataView()RatelModelParameterDataView()RatelMaterialDestroy()RatelMaterialGetActiveFieldSizes()RatelMaterialGetPointFields()RatelMaterialGetNumOutputFieldsComponents()RatelMaterialGetActiveFieldNames()RatelMaterialGetOutputFieldsComponentNames()RatelMaterialGetVolumeLabelName()RatelMaterialGetVolumeLabelValues()RatelMaterialSetVolumeLabelValue()RatelMaterialGetForcingType()RatelMaterialGetMaterialName()RatelMaterialGetModelName()RatelMaterialGetSurfaceGradientLabelName()RatelMaterialGetSurfaceGradientOutputFieldsLabelName()RatelMaterialGetSurfaceGradientOperatorFaceLabelAndValue()RatelMaterialGetInitialRandomScaling()RatelMaterialHasMMS()RatelMaterialGetCLPrefix()RatelMaterialGetModelFormulation()RatelMaterialGetCLMessage()RatelMaterialCreateOperatorName()RatelMaterialGetSolutionData()RatelMaterialGetStoredDataU()RatelMaterialGetStoredDataUt()RatelMaterialGetStoredDataUtt()RatelMaterialGetInitialStateData()RatelMaterialGetStateData()RatelMaterialGetPointData()RatelMaterialSetOperatorName()RatelMaterialCreateRandomParameters()RatelMaterialGetVolumeQData()RatelMaterialGetMeshVolumeQData()RatelMaterialGetSurfaceGradientQData()RatelMaterialGetSurfaceGradientOutputFieldsQData()RatelMaterialSetupResidualSuboperators()RatelMaterialSetupJacobianSuboperator()RatelMaterialSetupJacobianBlockSuboperator()RatelMaterialSetBoundaryJacobianMultigridInfo()RatelMaterialSetupMultigridLevel()RatelMaterialAcceptState()RatelMaterialSetupStrainEnergySuboperator()RatelMaterialSetupOutputFieldsSuboperators()RatelMaterialSetupSurfaceForceCellToFaceSuboperators()RatelMaterialSetupMMSErrorSuboperator()RatelRegisterModels()RatelModelDataVerifyRelativePath()RatelModelParameterDataGetDefaultValue_Scalar()RatelModelParameterDataGetDefaultValue_Int()RatelModelParameterDataGetDefaultValue_Bool()RatelModelParameterDataRegisterContextFields()RatelMaterialCreate_MPM()RatelMPMOptionsCreateFromOptions()RatelMaterialGetMPMContext()RatelMPMContextCreate()RatelMPMContextDestroy()RatelMPMContextGetPoints()RatelMPMContextGetElemRestrictionPoints()RatelMPMContextGetNumPointsLocal()RatelMPMContextCeedElemRestrictionCreateAtPoints()RatelMPMContextCeedOperatorSetPoints()RatelMaterialSetupMeshToSwarmSuboperators_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupMigratePointsSuboperator()RatelMPMMeshToSwarm()RatelMaterialSetupSwarmToMeshSuboperators_MPM()RatelMPMProjectionResultView()RatelMPMSwarmToMesh()RatelMPMSetVolume()RatelMaterialSetupUpdateVolumeSuboperator_MPM()RatelMPMUpdateVolume()RatelSolutionDMSetup_MPM()RatelDMSetupByOrder_MPM()RatelMaterialReset_MPM()RatelMPMReset()RatelMPMMigrate()RatelMaterialSetupVolumeQData_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupResidualSuboperators_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupJacobianSuboperator_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupJacobianBlockSuboperator_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupMMSErrorSuboperator_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupForcingSuboperator_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupForcingEnergySuboperator_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupStrainEnergySuboperator_MPM()RatelMaterialSetupOutputFieldsSuboperators_MPM()RatelMPMComputeMaterialBoundaryLabel()RatelMaterialCreate_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageCurrentPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageInitialPrincipal()RatelMaterialCreate_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()RatelRegisterModel_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipal()RATEL_MAX_FIELDSRATEL_MAX_MATERIAL_SIZEQ_DATA_SURFACE_FORCE_GEOMETRY_SIZEQ_DATA_SURFACE_GEOMETRY_SIZEQ_DATA_VOLUMETRIC_GEOMETRY_MPM_SIZEQ_DATA_VOLUMETRIC_SYMMETRIC_GEOMETRY_MPM_SIZEQ_DATA_VOLUMETRIC_SYMMETRIC_GEOMETRY_SIZEQ_DATA_VOLUMETRIC_GEOMETRY_SIZENUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_DualNUM_COMPONENTS_ELASTICITY_output_fields_DualNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_ElasticityHenckyFLOPS_HenckyStrainFLOPS_HenckyStrain_fwdFLOPS_HenckyKirchhoffTauFLOPS_HenckySecondKirchhoffStressFLOPS_HenckySecondKirchhoffStress_fwdFLOPS_Hencky_dbedF_SymmetricFLOPS_Hencky_dedb_EigenvaluesFLOPS_KirchhoffStressSymmetric_fwdNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalFLOPS_JACOBIAN_ElasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_ElasticityHenckyDamageNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_ElasticityHenckyDamage_DualFLOPS_PsiPlus_HenckyFLOPS_PsiPlus_Hencky_fwdNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalFLOPS_JACOBIAN_ElasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalFLOPS_Tau_IsochoricMooneyRivlinFLOPS_S_IsochoricMooneyRivlinFLOPS_dS_IsochoricMooneyRivlinFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_IsochoricMooneyRivlinNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrentFLOPS_df1_IsochoricMR_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_IsochoricMooneyRivlinCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitialFLOPS_df1_IsochoricMR_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_IsochoricMooneyRivlinInitialFLOPS_Tau_IsochoricNeoHookeanFLOPS_S_IsochoricNeoHookeanFLOPS_dS_IsochoricNeoHookeanFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_IsochoricNeoHookeanFLOPS_StrainEnergy_IsochoricNeoHookeanNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df1_IsochoricNH_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_IsochoricNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_df1_IsochoricNH_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_IsochoricNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_Tau_IsochoricOgdenFLOPS_S_IsochoricOgdenFLOPS_dS_IsochoricOgdenFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_IsochoricOgdenFLOPS_Tau_IsochoricOgden_fwdNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_EnzymeNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_IsochoricOgdenCurrentAD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_IsochoricOgdenCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_IsochoricOgdenCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_IsochoricOgdenCurrentFLOPS_df1_IsochoricOgden_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_IsochoricOgdenCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_IsochoricOgdenInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_IsochoricOgdenInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_IsochoricOgdenInitialFLOPS_df1_IsochoricOgden_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_IsochoricOgdenInitialFLOPS_Tau_iso_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_S_iso_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_dS1_iso_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_dS2_iso_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_dS3_iso_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_dS_iso_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_iso_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_J_powFLOPS_Tau_iso_NeoHookeanFLOPS_S_iso_NeoHookeanFLOPS_dS_iso_NeoHookeanFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_iso_NeoHookeanFLOPS_Tau_iso_OgdenFLOPS_S_iso_OgdenFLOPS_dS_iso_OgdenFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_iso_OgdenFLOPS_Tau_iso_Ogden_fwdFLOPS_PsiPlus_LinearFLOPS_PsiPlus_Linear_fwdFLOPS_DegradedStress_LinearFLOPS_DegradedStress_Linear_fwdFLOPS_df0_DamageLinearFLOPS_df1_u_DamageLinearFLOPS_df1_phi_DamageLinearFLOPS_df1_DamageLinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Elasticity_DamageFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Elasticity_Damage_ContactNUM_COMPONENTS_ELASTICITY_LINEAR_output_fields_DualNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_LinearNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_LinearNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_LinearNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_LinearFLOPS_df1_LinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_LinearNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanFLOPS_PhiAniso_BaseFLOPS_PhiAnisoFLOPS_dPhiAnisoFLOPS_d2PhiAnisoFLOPS_StructureTensor_CurrentFLOPS_Tau_anisotropic_NeoHookeanFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_anisotropic_NeoHookeanFLOPS_Tau_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrent_pNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df1_MixedAnisotropicNH_CurrentFLOPS_dg0_MixedAnisotropicNH_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_MixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MixedLinearNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MixedLinearNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedLinear_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedLinear_pNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedLinearNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_MixedLinearFLOPS_df1_MixedLinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MixedLinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_MixedLinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_MixedLinearFLOPS_Tau_MixedNeoHookeanFLOPS_S_MixedNeoHookeanFLOPS_dS_MixedNeoHookeanFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_MixedNeoHookeanNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MixedNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MixedNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanCurrent_pNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df1_MixedNH_CurrentFLOPS_dg0_MixedNH_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MixedNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_MixedNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_MixedNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MixedNeoHookeanInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MixedNeoHookeanInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanInitial_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanInitial_pNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_df1_MixedNH_InitialFLOPS_dg0_MixedNH_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MixedNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_MixedNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_MixedNeoHookeanInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_MixedNeoHookeanPLFLOPS_Tau_MixedNeoHookeanPLFLOPS_S_MixedNeoHookeanPLFLOPS_dS_MixedNeoHookeanPLFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_MixedNeoHookeanPLNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrent_pNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrentFLOPS_df1_MixedNHPL_CurrentFLOPS_dg0_MixedNHPL_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_MixedNeoHookeanPLCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitial_pNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitialFLOPS_df1_MixedNHPL_InitialFLOPS_dg0_MixedNHPL_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_MixedNeoHookeanPLInitialFLOPS_Tau_MixedOgdenFLOPS_S_MixedOgdenFLOPS_dS_MixedOgdenNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MixedOgdenInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MixedOgdenInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedOgdenInitial_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedOgdenInitial_pNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MixedOgdenInitialFLOPS_df1_MixedOgden_InitialFLOPS_dg0_MixedOgden_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MixedOgdenInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_MixedOgdenInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_MixedOgdenInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_MixedElasticityFLOPS_Tau_vol_mixed_PLFLOPS_S_vol_mixed_PLFLOPS_dS_vol_mixed_PLFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_vol_mixed_PLFLOPS_Tau_vol_mixedFLOPS_S_vol_mixedFLOPS_dS_vol_mixedFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_vol_mixedFLOPS_Tau_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_S_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_dS_MooneyRivlinFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_MooneyRivlinNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MooneyRivlinCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MooneyRivlinCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MooneyRivlinCurrentFLOPS_df1_MR_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MooneyRivlinCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MooneyRivlinInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MooneyRivlinInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MooneyRivlinInitialFLOPS_df1_MR_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MooneyRivlinInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_ELASTICITY_output_fields_Dual_MPMNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_MPM_NeoHookeanNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrentNUM_POINTS_FIELDS_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df1_MPM_NH_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df0_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPMFLOPS_df1_u_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPMFLOPS_df1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPMFLOPS_df1_DamageNeoHookeanCurrent_MPMFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MPM_NeoHookeanCurrent_DamageNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPreviousNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPreviousNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPreviousNUM_POINTS_FIELDS_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPreviousNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPreviousFLOPS_df1_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPreviousFLOPS_JACOBIAN_MPM_TriclinicAnisotropicPreviousFLOPS_Tau_NeoHookeanFLOPS_S_NeoHookeanFLOPS_dS_NeoHookeanFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_NeoHookeanNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookeanCurrent_AD_ADOLCNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanCurrent_AD_ADOLCNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookeanCurrent_AD_ADOLCNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_EnzymeNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookeanCurrentAD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df1_NH_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_NeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_NeoHookean_Damage_DualNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_NeoHookean_DamageNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookean_DamageNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookean_DamageNUM_U_t_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookean_DamageFLOPS_PsiPlus_NeoHookeanFLOPS_PsiPlus_NeoHookeanInitial_fwdFLOPS_Degraded_S_NeoHookeanFLOPS_Degraded_dS_NeoHookeanFLOPS_Degraded_Tau_NeoHookeanFLOPS_PsiPlus_NeoHookeanCurrent_fwdFLOPS_Degraded_FdSFTranspose_NeoHookeanFLOPS_df1_u_DamageNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_df1_DamageNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_NeoHookeanCurrent_DamageFLOPS_df0_DamageNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_df1_u_DamageNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_df1_phi_DamageNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_df1_DamageNeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_NeoHookeanInitial_DamageFLOPS_JACOBIAN_NeoHookeanInitial_Damage_ContactNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_ADOLCNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_ADOLCNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_ADOLCRATEL_ELASTICITY_NEO_HOOKEAN_INITIAL_AD_TAPE_SIZENUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_EnzymeNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookeanInitial_AD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookeanInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookeanInitialFLOPS_df1_NH_InitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_NeoHookeanInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent_utNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrentFLOPS_df1_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrent_CurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_NeoHookeanShockScalarCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_ElasticityFLOPS_Tensor4MatMultSymFLOPS_VecRotateRodriguesSymmetricFLOPS_MatRotationRodriguesNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_TriclinicAnisotropicInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_TriclinicAnisotropicInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_TriclinicAnisotropicInitialFLOPS_df1_TriclinicAnisotropicInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_TriclinicAnisotropicInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_UHyperNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_UHyperFLOPS_VFLOPS_J_dVdJFLOPS_J2_d2VdJ2FLOPS_UFLOPS_J_dUdJFLOPS_J2_d2UdJ2FLOPS_Tau_volFLOPS_S_volFLOPS_dS_volFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_volFLOPS_LogStrainInelasticity_dbedF_SymmetricFLOPS_LogStrainInelasticity_dedb_EigenvaluesFLOPS_LogStrainInelasticity_KirchhoffStressSymmetric_fwdFLOPS_LogStrainInelasticity_dlogAdA_SymmetricFLOPS_ReturnMapping_vonMisesLinear_fwdFLOPS_ReturnMapping_vonMisesPricipal_fwdNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_PlasticityHencky_AdditiveNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_PlasticityHenckyNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_EnzymeNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveAD_EnzymeNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PlasticityHenckyCurrentAdditiveNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalFLOPS_JACOBIAN_PlasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PlasticityHenckyCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PlasticityHenckyCurrentNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PlasticityHenckyCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_PlasticityHenckyCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_PlasticityHenckyDamageNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalFLOPS_JACOBIAN_PlasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PlasticityHenckyInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PlasticityHenckyInitialNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PlasticityHenckyInitialFLOPS_JACOBIAN_PlasticityHenckyInitialNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PlasticityLinearNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PlasticityLinearNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PlasticityLinearNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_PlasticityLinearNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PoromechanicsLinearNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PoromechanicsLinearNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PoromechanicsLinear_utNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PoromechanicsLinear_uttNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsLinear_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsLinear_pfNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsLinearNUM_U_t_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsLinear_uNUM_U_t_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsLinear_pfNUM_U_tt_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsLinear_uNUM_U_tt_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsLinear_pfNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_PoromechanicsLinearFLOPS_df1_PoromechanicsLinearFLOPS_dg0_PoromechanicsLinearFLOPS_dg1_PoromechanicsLinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_PoromechanicsLinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_PoromechanicsLinearFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_PoromechanicsLinearFLOPS_PoreFluidDensityFLOPS_PorosityFunctionKozenyCarmanFLOPS_PorosityFunctionKozenyCarman_fwdFLOPS_PorosityFunctionHyperbolicFLOPS_PorosityFunctionHyperbolic_fwdFLOPS_Tau_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanFLOPS_FdSFTranspose_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_utNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_uttNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_uNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_pfNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_U_t_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_uNUM_U_t_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_pfNUM_U_tt_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_uNUM_U_tt_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrent_pfFLOPS_df1_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_dg0_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_dg1_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_uu_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentFLOPS_JACOBIAN_Block_pp_PoromechanicsNeoHookeanCurrentNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_ViscoelasticityHenckyFLOPS_LogStrainInelasticity_MaxwellElement_DeviatoricStrainUpdate_fwdNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalFLOPS_JACOBIAN_ViscoelasticityHenckyCurrentPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_OUTPUT_FIELDS_ViscoelasticityHenckyDamageNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalNUM_ACTIVE_FIELD_EVAL_MODES_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalFLOPS_JACOBIAN_ViscoelasticityHenckyInitialPrincipalRatelMaskSetBitRatelModelParameterRatelCommonParamsRatelElasticityDamageParamsRatelLinearElasticityParamsRatelMixedLinearElasticityParamsRatelTriclinicAnisotropicElasticityParamsRatelMixedOgdenElasticityParamsRatelMMSCEEDBPsParamsRatelMMSLinearElasticityParamsRatelMMSPoromechanicsLinearParamsRatelMooneyRivlinElasticityParamsRatelShockParamsRatelNeoHookeanShockScalarElasticityParamsRatelOgdenElasticityParamsRatelPlasticityDamageParamsRatelPlasticityParamsRatelElastoPlasticityParamsRatelLinearPoromechanicsParamsRatelNeoHookeanPoromechanicsParamsRatelViscoelasticityDamageParamsRatelViscosityParamsRatelViscoelasticityParamsRatelBoundingBoxParamsRestrictionContextRatelElasticityDamagePointFieldsRatelLinearElasticityPointFieldsRatelHenckyElasticityParamsRatelHenckyElasticityPointFieldsRatelMixedAnisotropicNeoHookeanElasticityParamsRatelNeoHookeanElasticityParamsRatelMMSMixedLinearElasticityParamsRatelNeoHookeanShockScalarElasticityPointFieldsRatelNeoHookeanElasticityPointFieldsRatelViscoelasticityPointFieldsRatelMPMContextRatelModelParameterDataRatelModelDataRatelMaterial
Boundary conditions¶
These functions apply boundary conditions.
- Boundary Conditions
RatelCrossingTypeRatelBoundaryTypeRatelContactShapeTypeRatelFrictionTypeRatelBCInterpolationTypeRatelContactEnforcementTypeRatelBCFunctionRatelBCContactProjectRatelBCContactProject_fwdRatelBCContactUpdateModelRatelBCContactFrictionRatelBCContactFriction_fwdRatelBoundaryTypesRatelContactShapeTypesRatelContactShapeTypesCLRatelFrictionTypesRatelFrictionTypesCLRatelBCInterpolationTypesRatelBCInterpolationTypesCLRatelContactEnforcementTypesRatelContactEnforcementTypesCLClampBCs()SetupDirichletBCs()RatelBCInterpGetPreviousKnotIndex()RatelBCInterpScaleTime()RatelBCInterpolate()ContactBCs_AugmentedLagrangian_ConstraintError()ContactBCs_AugmentedLagrangian()ContactBCs_AugmentedLagrangian_Jacobian()RatelContactTranslate()RatelBCContactGap()RatelBCContactGap_fwd()RatelBCContactSlipVelocity()RatelBCContactSlipVelocity_fwd()RatelBCContactProject_Cylinder()RatelBCContactProject_fwd_Cylinder()RatelBCContactUpdateModel_Cylinder()FrictionCoulomb()FrictionCoulomb_fwd()FrictionThrelfall()FrictionThrelfall_fwd()FrictionNone()FrictionNone_fwd()ContactBCs_Nitsche()ContactBCs_Nitsche_Jacobian()SetupSurfaceGeometrySplit()ContactBCs_Penalty()ContactBCs_Penalty_Jacobian()RatelBCContactProject_Platen()RatelBCContactProject_fwd_Platen()RatelBCContactUpdateModel_Platen()PressureBCs()PressureBCsJacobian()SetupSlipBCs()SlipBCs()TractionBCs()TractionEnergy()MMSBCs_CEED_ScalarBPs()MMSBCs_CEED_VectorBPs()MMSBCs_Linear()MMSBCs_MixedLinear()MMSBCs_PoromechanicsLinear_u()MMSBCs_PoromechanicsLinear_pf()MMSError_MixedLinear()MMSError_PoromechanicsLinear()RatelBoundaryClampDataFromOptions()RatelBoundaryClampSetupDirichletSuboperators()RatelFrictionParamsView()RatelFrictionParamsCheck_Coulomb()RatelFrictionParamsCheck_Threlfall()RatelFrictionParamsFromOptions()RatelBoundaryContactPlatenParamsView()RatelBoundaryContactCylinderParamsView()RatelBoundaryPlatenParamsFromOptions()RatelBoundaryCylinderParamsFromOptions()RatelBoundaryContactParamsView()RatelBoundaryContactParamsCommonFromOptions()RatelBoundaryContactParamsFromOptions()RatelBoundaryContactContextRegisterMaterialFields()RatelBoundaryContactRegisterCommonFields()RatelBoundaryContactRegisterShapeFields_Platen()RatelBoundaryContactRegisterShapeFields_Cylinder()RatelBoundaryContactCeedContextCreate()RatelBoundaryContactCeedContextCreateFromOptions()RatelBoundaryContactNitscheSetupMaterialSuboperators()RatelBoundaryContactPenaltySetupSuboperators()RatelBoundaryContactAugmentedLagrangianSetupSuboperators()RatelBoundaryMMSSetupDirichletSuboperators()RatelBoundaryPressureParamsFromOptions()RatelBoundaryPressureParamsView()RatelBoundaryPressureSetupSuboperators()RatelCreateBCLabel()RatelDMAddBoundariesDirichlet()RatelBoundarySetupMultigridLevel_Standard()RatelBoundarySetupMultigridLevel_CellToFace()RatelBoundarySetupDirichletSuboperators()RatelBoundarySetupSuboperators()RatelBoundarySetupMaterialSuboperators()RatelBoundarySetupEnergySuboperators()RatelSetupSurfaceQData()RatelSetupSurfaceForceCentroids()RatelBoundarySetupSurfaceDisplacementSuboperators()RatelBoundingBoxParamsFromOptions()RatelFaceLabelValueFromOptions()RatelFaceLabelValuesFromOptions()RatelBoundaryTractionParamsFromOptions()RatelBoundaryTractionParamsView()RatelBoundaryTractionSetupSuboperators()RatelBoundaryTractionSetupEnergySuboperators()RATEL_MAX_BC_INTERP_POINTSFLOPS_BCInterpScaleTimeFLOPS_BCInterpolate_BaseFLOPS_BCInterpolate_PerDimRATEL_MAX_CONTACT_MODEL_SIZERATEL_MAX_VERTICES_PER_CLIPPED_POLYGONRATEL_MAX_CLIPPED_POLYGONSRATEL_MAX_MORTAR_QORDERRATEL_MAX_MORTAR_QPOINTSNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_Contact_AugmentedLagrangianNUM_COMPONENTS_STATE_Contact_AugmentedLagrangianFLOPS_Contact_AugmentedLagrangian_JacobianFLOPS_ContactTranslateFLOPS_ContactGapFLOPS_ContactGap_fwdFLOPS_ContactSlipVelocity_fwdFLOPS_ContactProject_CylinderFLOPS_ContactProject_fwd_CylinderFLOPS_FrictionCoulombFLOPS_FrictionCoulomb_fwdFLOPS_FrictionThrelfallFLOPS_FrictionThrelfall_fwdNUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_Contact_NitscheFLOPS_Contact_Nitsche_Jacobian_without_df1NUM_COMPONENTS_STORED_Contact_PenaltyFLOPS_Contact_Penalty_JacobianFLOPS_ContactProject_PlatenFLOPS_ContactProject_fwd_PlatenFLOPS_Jacobian_PressureBCRatelBCClampParamsRatelFrictionParamsRatelBCContactParamsCommonRatelBCContactParamsRatelBCContactCylinderParamsRatelBCContactPlatenParamsRatelPolygonVertex_privateRatelPolygonRatelClippedPolygon2DRatelClippedPolygonListRatelLocalCoordinateSpaceRatelTriangulationRatelSegmentationContextRatelBCPressureParamsRatelBCSlipParamsRatelBCTractionParamsRatelBoundingBoxParamsRatelPolygonVertex
Internal functions¶
These functions are internal setup and application functions.
- Internal Functions
RatelTSMonitorFunctionConstRatelPolygonVertexenzyme_tapeenzyme_constenzyme_dupenzyme_nofreeenzyme_allocated__enzyme_function_likeRATEL_CLASSIDRATEL_SetupRATEL_DMSetupByOrderRATEL_DMSetupSolverRATEL_OutputFieldsRATEL_OutputFields_CeedOpRATEL_ResidualRATEL_Residual_CeedOpRATEL_JacobianRATEL_Jacobian_CeedOpRATEL_MPM_MigrateRATEL_MPM_SwarmToMeshRATEL_MPM_SwarmToMesh_CeedOpRATEL_RemapMeshRATEL_MonitorRATEL_CeedBasisCreateRATEL_CeedElemRestrictionCreateRATEL_CeedElemRestrictionCreatePointsRATEL_SetupResidualRATEL_SetupJacobianMemTypePetscToCeed()GetCeedQuadratureSize()MMSError_CEED_ScalarBPs()MMSError_CEED_VectorBPs()MMSError_Linear()BodyForce()BodyForceEnergy()MMSForce_CEED_BP1()MMSForce_CEED_BP2()MMSForce_CEED_BP3()MMSForce_CEED_BP4()MMSForce_Linear()MMSForceEnergy_Linear()MMSForce_MixedLinear()MMSForceEnergy_MixedLinear()MPMBodyForce()MMSForce_PoromechanicsLinear()MMSICs_PoromechanicsLinear_u()MMSICs_PoromechanicsLinear_pf()Mass()RatelScalarBPsMMSTrueSolution()RatelScalarBPsPoissonForcing()RatelVectorBPsMMSTrueSolution()RatelVectorBPsPoissonForcing()RatelLinearElasticityMMSTrueSolution()RatelLinearElasticityMMSForcing()RatelMixedLinearElasticityMMSTrueSolution()RatelMixedLinearElasticityMMSForcing()RatelPoromechanicsMMSTrueSolution()RatelPoromechanicsMMSForcing()RatelPoromechanicsMMSGamma()__enzyme_autodiff()__enzyme_fwddiff()__enzyme_augmentfwd()__enzyme_fwdsplit()__enzyme_augmentsize()ElasticityResidual_utt()ElasticityDamageResidual_utt()RatelComputeJ2m1_ADOLC()RatelMatTraceSymmetric_ADOLC()RatelLog1p_ADOLC()RatelStrainEnergy_NeoHookean_AD_ADOLC()GradientPsi_ADOLC()HessianPsi_ADOLC()PoromechanicsLinearResidual_utt()PoromechanicsResidual_utt()RatelMigratePoints()ScaleLumpedDualOutputFieldsTerms()ScaledMass()ComputeCentroid()RatelOrient2DRobustSingle()RatelOrient2D()RatelCoordinatesInBoundingBox()RatelLog1p()RatelLog1pMinusx()RatelExpm1Series()RatelAtanSeries()RatelSign()RatelStoredValuesPack()RatelStoredValuesUnpack()RatelDot3()RatelNorm3()RatelScalarVecMult()RatelVecVecAdd()RatelVecVecVecAdd()RatelVecVecSubtract()RatelVecVecCross()RatelVecOuterMult()RatelVecVecOuterMult()RatelScalarMatMult()RatelScalarMatMultSymmetric()RatelMatVecMult()RatelMatTransposeVecMult()RatelSymmetricMatPack()RatelSymmetricMatUnpack()RatelMatTrace()RatelMatTraceSymmetric()RatelMatMatAdd()RatelMatMatAddSymmetric()RatelMatMatMatAddSymmetric()RatelMatMatMatAdd()RatelMatDeviatoricSymmetric()RatelMatMatMult()RatelMatTransposeMatMult()RatelMatMatTransposeMult()RatelMatTransposeMatTransposeMult()RatelMatMatMultPlusMatMatMult()RatelMatMatContractSymmetric()RatelMatDetA()RatelComputeJm1()RatelComputeJ2m1()RatelJ2m1m2TraceE()RatelMatMatMultSymmetric()RatelMatNorm()RatelMatMatMatMultSymmetric()RatelMatMatSymmetricMatTransposeMult()RatelMatTransposeMatSymmetricMatMult()RatelMatInverse()RatelMatInverseSymmetric()RatelScaledMassApplyAtQuadraturePoint()RatelCInverse()RatelCInverse_fwd()RatelLinearStrain()RatelLinearStrain_fwd()RatelGreenEulerStrain()RatelGreenEulerStrain_fwd()RatelGreenLagrangeStrain()RatelGreenLagrangeStrain_fwd()RatelLinearStress()RatelLinearStress_fwd()RatelMixedLinearStress()RatelMixedLinearStress_fwd()RatelPoromechanicsLinearStress()RatelPoromechanicsLinearStress_fwd()RatelOrthogonalComplement()RatelComputeEigenvector0()RatelComputeEigenvector1()RatelMatComputeEigensystemSymmetric()RatelEigenValue_fwd()RatelEigenVector_fwd()RatelPrincipalStretch()RatelPrincipalStretch_fwd()RatelEigenVectorOuterMult()RatelEigenVectorOuterMult_fwd()RatelVecSignum()RatelVecSignum_fwd()RatelMatFromEigensystemSymmetric()RatelQdataUnpack()RatelQdataPack()RatelGradUnpack()RatelMatMatMultAtQuadraturePoint()RatelMatMatTransposeMultAtQuadraturePoint()RatelMatMatTransposeMultAtQuadraturePoint4x3()RatelMatVecMultAtQuadraturePoint()RatelProcessCommandLineOptions()RatelCheckViewOptions()RatelDMCeedVectorDestroy()RatelDMPlexCeedElemRestrictionDestroy()RatelDMPlexCeedBasisDestroy()RatelIncrementMeshRemapState()RatelGetMeshRemapState()RatelRemapScale_inner()RatelRemapScale()RatelSetRemapScaleParametersFromOptions()RatelRemapScaleCoordinates()RatelTransition()RatelTransformRightBoundary_1D()RatelTransformLeftBoundary_1D()RatelKershaw()RatelDMPlexCreateFromOptions()RatelDMSwarmClearCellIds()RatelDMSwarmCreateFromOptions()RatelDMSwarmInitializePointLocations()RatelDMSwarmLoadField()RatelDMSwarmLoadFromCheckpoint()RatelDMGetDomainISLocal()RatelDMGetCoordinatesLocalCeed()RatelDMDestroyCoordinatesLocalCeed()RatelDMGetCoordinatesLocalOriginalCeed()RatelDMSwarmCreateReferenceCoordinates()RatelDMSwarmCeedElemRestrictionPointsCreate()RatelDMSwarmViewFromOptions()RatelGetSolutionMeshDM()RatelGetEnergyDM()RatelDMPlexCreateFaceLabel()PetscDTUniformTensorQuadrature()PetscFECreateLagrangeSpacesFromOptions()PetscFECreateLagrangeFromOptions()PetscFECreateUniformFromOptions()RatelFECreateFromOptions()RatelDMFieldToDSField()RatelGetClosurePermutationAndFieldOffsetAtDepth()RatelGetQuadratureDataP2C()RatelCreate1DTabulation_Tensor()RatelComputeFieldTabulationP2C()RatelGetGlobalDMPolytopeType()RatelDMPlexCeedBasisCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedBasisCoordinateCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedBasisCellToFaceCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedBasisCellToFaceCoordinateCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedElemRestrictionCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedElemRestrictionCoordinateCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedElemRestrictionStridedCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedElemRestrictionQDataCreate()RatelDMPlexCeedElemRestrictionCollocatedCreate()RatelDMGetFieldISLocal()RatelDMHasFace()RatelForcingBodyParamsFromOptions()RatelMaterialForcingBodyDataFromOptions()RatelMaterialSetupForcingSuboperator()RatelMaterialSetupForcingEnergySuboperator()RatelCreateSubmatrix()RatelSNESSetJacobianMats()RatelSNESAugmentedLagrangianConstraintError()RatelSNESAugmentedLagrangianUpdate()RatelSNESAugmentedLagrangianAcceptState()RatelSNESAugmentedLagrangianResetDeltaState()RatelSNESFormResidual()RatelSNESFormJacobian()RatelTSFormIResidual()RatelTSFormIJacobian()RatelTSFormI2Residual()RatelTSFormI2Jacobian()RatelTSPreStep()RatelTSPreStage()RatelTSPostEvaluate()RatelTSPostStep()RatelSNESFormObjective()RatelIncrementalize()RatelGetGitVersion()RatelGetBuildConfiguration()RatelSetupStrainEnergyEvaluator()RatelSetupExternalEnergyEvaluator()RatelSetupOutputFieldsEvaluators()RatelSetupMMSErrorEvaluator()RatelSetupSurfaceDisplacementEvaluators()RatelSetupFaceRestrictionNodalOperator()RatelSetupSurfaceForceEvaluator()RatelSetupSurfaceForceCellToFaceEvaluators()RatelComputeOutputFields_Internal()RatelComputeSurfaceForcesCellToFace_Internal()RatelComputeSurfaceForces_Internal()RatelComputeSurfaceCentroids_Internal()PetscCallCeedRatelCallCeedRatelLoggerLogGenericRatelLoggerLogTraceRatelLoggerLogDebugRatelLoggerLogInfoRatelLoggerLogWarnRATEL_MAX_FORCE_INTERP_POINTSRATEL_PI_DOUBLERATEL_EPSILON_DOUBLERatelMaxRatelMinRatelMaskBitIsSetRatelSetOutputRatelValueInIntervalFLOPS_Orient2DRobustSingleFLOPS_Orient2DFLOPS_dXdxwdetJFLOPS_ScaledMassFLOPS_Log1pFLOPS_Log1pMinusxFLOPS_Expm1SeriesFLOPS_AtanSeriesFLOPS_Dot3FLOPS_Norm3FLOPS_ScalarVecMultFLOPS_VecVecAddFLOPS_VecVecVecAddFLOPS_VecVecSubtractFLOPS_VecVecCrossFLOPS_VecOuterMultFLOPS_VecVecOuterMultFLOPS_ScalarMatMultFLOPS_ScalarMatMultSymmetricFLOPS_MatVecMultFLOPS_MatTransposeVecMultFLOPS_MatTraceFLOPS_MatMatAddFLOPS_MatMatAddSymmetricFLOPS_MatMatMatAddSymmetricFLOPS_MatMatMatAddFLOPS_MatDeviatoricSymmetricFLOPS_MatMatMultFLOPS_MatMatTransposeMultFLOPS_MatMatMultPlusMatMatMultFLOPS_MatMatContractSymmetricFLOPS_MatDetAFLOPS_JM1FLOPS_J2m1m2TraceEFLOPS_MatMatMultSymmetricFLOPS_MatNormFLOPS_MatMatMatMultSymmetricFLOPS_MatMatSymmetricMatTransposeMultFLOPS_MatTransposeMatSymmetricMatMultFLOPS_MatInverseFLOPS_MatInverseSymmetricFLOPS_CInverseFLOPS_CInverse_fwdFLOPS_LinearStrainFLOPS_LinearStrain_fwdFLOPS_GreenEulerStrainFLOPS_GreenEulerStrain_fwdFLOPS_GreenLagrangeStrainFLOPS_GreenLagrangeStrain_fwdFLOPS_LinearStressFLOPS_LinearStress_fwdFLOPS_MixedLinearStressFLOPS_MixedLinearStress_fwdFLOPS_PoromechanicsLinearStressFLOPS_PoromechanicsLinearStress_fwdFLOPS_OrthogonalComplementFLOPS_ComputeEigenvector0FLOPS_ComputeEigenvector1FLOPS_MatComputeEigenValueSymmetricFLOPS_MatComputeEigenVectorSymmetricFLOPS_MatComputeEigensystemSymmetricFLOPS_EigenValue_fwdFLOPS_EigenVector_fwdFLOPS_PrincipalStretchFLOPS_PrincipalStretch_fwdFLOPS_EigenVectorOuterMultFLOPS_EigenVectorOuterMult_fwdFLOPS_VecSignumFLOPS_VecSignum_fwdFLOPS_MatFromEigensystemSymmetricRATEL_output_fields_PROJECTION_SCALAR_FIELD_NAMERATEL_output_fields_PROJECTION_SCALAR_LABEL_NAMERATEL_output_fields_PROJECTION_SCALAR_LABEL_VALUERATEL_output_fields_PROJECTION_SCALAR_LABEL_VALUE_STRINGRATEL_output_fields_PROJECTION_SCALAR_OPTION_NAMERATEL_output_fields_PROJECTION_FULL_DIAGONAL_NAMERatelLammpsPointRatelLogger_privateRatelForcingBodyParamsRatelScaledMassParamsRatelLoggerRatelPMGContextRatelVoxelRatelMPMStabilizationRatelViewerRatelViewersRatelCheckpointCtxRatelCheckpointDataRatelMPMOptions